Between the Rockies and the Coast Mountains the native peoples occupied valleys and plateaus plateau: a flat plain in the mountains or at a height above sea level. where they encountered both desert and forest enviroments. Important to their lives were the major rivers that ran through this area - the Fraser, Thompson and Columbia. The tribal groups were called Interior Salish (including sub-groups: Lillooet, Thompson, Okanagan and Shuswap), the Kutenai (Ktunaxa) and the Chilcotin (Tsilhqot'in).
FOOD AND ECONOMY
One of the most important food sources for the Plateau peoples was the salmon which teemed up the rivers during spawning spawn: to produce eggs, give birth to. season - late summer and fall. These were caught with nets, harpoons, spears or traps. It was the women's job to fillet and dry the fish. The Plateau nations also hunted and gathered plant food, sometimes digging up roots with hardwood digging sticks. The more northern Kutenai would cross the mountains to hunt buffalo, which brought them into conflict with the Plains Blackfoot. The Salish carried on some trade with the coast tribes acquiring dentalium dentalium: a tubular shell found on the west coast, used for ornamentation and traded to interior tribes. shells which were used along with porcupine quills to decorate clothing. The Salish women were skilled weavers and the "Salish loom" is still used by weavers in Canada today.
DWELLINGS
The interior Salish dug pit-houses into the ground in winter. Only the dome roof, fashioned from log rafters, was above the surface. These houses were entered by a ladder leading down through the smoke hole. In summer they lived in bark-covered tipis. The mountain-dwelling Kutenai lived in skin-covered tipis. In winter they made larger lodges where several families lived together. 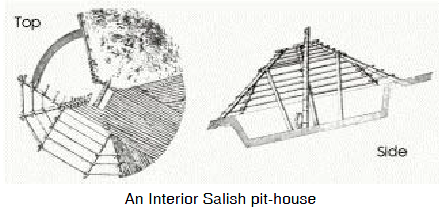
TRANSPORTATION
The canoe was a common means of transportation although it was used mostly to travel on lakes because the large rivers were too rough. The Kutenai had a very distinctive design - the "sturgeon-nosed" canoe - which was pointed at both ends. In winter the Plateau people travelled on snowshoes. Dogs were commonly used to help transport their belongings.
SOCIAL ORGANIZATION

These were fairly classless societies with the village chief chosen for his abilities by a council of elders. The chief could persuade, but not force his people and most adult males had a voice in decision-making.
RELIGION AND FESTIVALS
At puberty the young Plateau men were sent out alone with no food to wait for a vision which would reveal their spiritual guardian. As in other native groups, the shamans shaman: a medicine man in North American native culture. Someone with special spiritual gifts and the ability to heal. had special supernatural powers which could be used either for good or for bad purposes. The Kutenai, who mixed Plateau and Plains beliefs, also held regular Sun Dances. For the Salish, "coyote" was a trickster and transformer, like "Nanibush" to the Ojibwa and "Raven" for the Haida.
